Q1. How Long Should a Car Battery Last?
A car battery’s lifespan can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of battery, driving behavior, environment, climate, maintenance, etc. The most commonly used lead-acid battery has an average lifespan of 1 to 5 years. However, some batteries may last longer, while others may fail sooner.
To extend the life of your car battery, it’s a good idea to get it tested frequently and change it as necessary. Your car’s electrical system should also be kept in good operating condition, and you should try to park your car in a place with comfortable temperatures.
Q2. Car Battery Can Be Recharged?
Just driving the car on a regular basis will recharge your car battery. Make sure your car starts every time without distressing. The alternator charges the battery while the engine is operating. Due to a weak battery, it will take a long time to charge, and it may not always be enough to charge a deeply drained battery fully.
It is better to call 800-VOLT (8658) for on-site car battery inspection and replacement service.

Q3. Can I Dispose of the Car Battery in a General Garbage Container?
No, most types of batteries, particularly rechargeable and automobile batteries, should not be disposed of in a general garbage container. Batteries contain chemicals and components that, if not disposed of properly, may be harmful to the environment.
When replacing your car battery with MR VOLT, we will collect the old battery and hand it over to the authorized collector for recycling.
Q4. Can Jumpstarting a Car Damage the Battery?
Since jumping a car doesn’t usually harm your car battery, there are a few safety measures and some hazards to be aware of…
Connecting the jumper cables with the positive and negative terminals in the wrong order may result in a short circuit, which might harm the battery, the electrical system, or even the vehicle involved. Make sure the connections are always appropriately connected, with positive to positive and negative to negative.
If the dead battery is very old or has a dead cell, jump-starting may not work and may put further strain on the already weak battery. In certain instances, it may be necessary to replace the battery. How do you jump-start a car?
Let’s make it simple by calling 800-VOLT (8658) for on-site car jump start service.

How To Choose the Best Car Battery?
Choosing the right car battery for your vehicle is essential for reliability and durability. Here are some important aspects to consider when choosing a car battery.
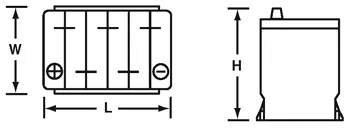
Battery Dimensions and Connectivity
Choose a battery compatible with the make, model, and engine type of your car. The battery’s group size and terminal arrangement should be correct. To determine the proper size and type, consult your car owner’s manual or call our expert at 800-VOLT (8658).
Reserve Capacity (RC) And Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
The reserve capacity of a battery determines how long it can operate without being recharged. Higher RC ratings are preferable for cars with a lot of electrical equipment. The CCA of a battery reflects its capacity to start the engine in cold conditions. Choose a battery with a CCA rating that meets or exceeds the needs of your vehicle, especially if you live in a cold or hot climate.
Warranty
Examine the warranty provided by the battery sellers. Longer warranties usually indicate that the manufacturer is confident in the battery’s durability and performance. Ensure you understand the warranty’s terms and conditions, including prorated coverage.
MR VOLT provides an extended warranty of up to 24 months.
Warranty Claim
Suppose you purchase the car battery from a nearby retailer. If your car battery is weak or dead while you are away from home, you may be unable to be covered by a warranty.
On-site battery replacement is the finest option for replacing your car battery, and it is simple to claim under your warranty term whenever and wherever.
Here we are, 800-VOLT (8658) on-site car battery replacement.

How to Jump Start A Car?
Jump-starting is a regular technique for starting a car with a dead or weak battery. Here’s how to jump-start a car safely.
Needs
- Another car with a functional battery.
- Jumper cables (also known as booster cables).
Parking
Both cars should be positioned with their faces towards each other and their batteries as close as possible without coming into contact. Ensure the ignition is off in both cars and in park or neutral (for manual transmissions).
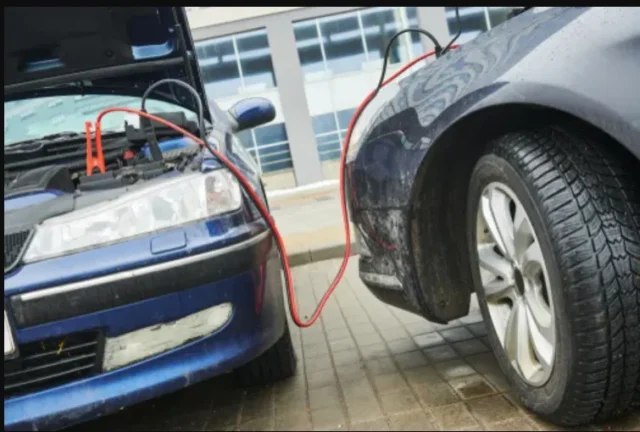

Prepare the Jumper Cables
- Let the two cars’ hoods open.
- Examine the two batteries. Verify that there are no leaks or cracks.
- Determine which battery’s positive (+) and negative (-) terminals are. Usually, they have labels. Normally red and may have a (+), the negative terminal is usually black and may have a (-).
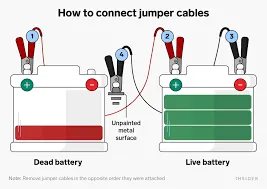
Connect the Jumper Cables
- The red (positive) jumper cable should first be connected to the positive terminal of the dead battery on one end.
- Connect the red jumper cable’s opposite end to the operational battery’s positive terminal.
- Attach the black jumper cable’s negative end to the functional battery’s negative terminal.
- The black jumper cable’s other end has to be attached to a metal surface on the dead automobile that isn’t painted, far from the battery. This reduces the possibility of sparking close to the battery by grounding the circuit.
Attempt to Start
Attempt to start the car with a dead battery. If it starts, that’s fantastic!
Allow it to run for a few minutes to fully charge the battery.
Remove the Jumper Cables
- Remove the black jumper cable from the previously dead car’s unpainted metal surface.
- Remove the black jumper cable from the working car’s negative terminal.
- Remove the red jumper cable from the working car’s positive terminal.
- Finally, remove the red jumper cable from the dead car’s positive terminal.

Keep the Car Running
Run the previously dead car for 10 to 15 minutes to ensure the battery is fully charged. Turn off the car.
Test the Car
Try to restart your car; if it starts, your jump-starting was successful.
If not starting, you should get expert help if you think there may be a more serious problem
with the battery or charging system.
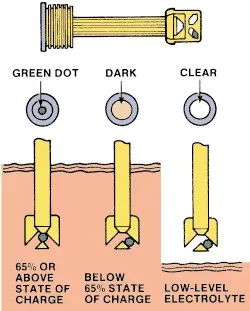
Car Battery Magic Eye
The “Car Battery Magic Eye” on a car battery is a simple state-of-charge indicator that offers a basic visual indication of the battery’s charge level. It usually consists of a tiny, transparent, green, or black gadget that fits on top of the battery.
How does it work?
The magic eye is normally green or black when the battery is in good condition and completely charged. It turns green when the battery’s acid density reaches an appropriate level.
If the charge level of the battery falls, the float inside the magic eye may fall, exposing a little red or white spot in the center of the eye. This often indicates a low level of charge and may indicate that the battery needs to be recharged.
If the float is not visible, it may indicate that the electrolyte level in the battery is too low. In these cases, the battery may need to be replaced or recharged with distilled water (if applicable)
What Battery Registration for AGM & EFB Batteries
Battery registration is a must when replacing an AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) or EFB (Enhanced Flooded Battery) in a modern car, especially one with advanced electronics and charging systems.
Battery registration ensures that the vehicle’s electrical system recognizes the new battery and adjusts its charging settings.
It might assist the BMS (Battery Management System) adjust the charging method and cycle time.
Replace the Battery Without Registration on BMS
You may change a car battery without properly registering it, but you should be aware of the potential implications.
You can replace the battery without registering older vehicles without modern charging and monitoring systems. Traditional flooded lead-acid batteries frequently do not require registration in older vehicles since their charging mechanisms are simpler and less sensitive to the battery’s kind and properties.
However, modern cars strongly suggest battery registration, particularly those equipped with advanced electrical systems, start-stop technology, and various battery types such as AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) or EFB (Enhanced Flooded Battery).

Battery Energy Management (BEM) Code
According to BMS technology, car manufacturers have decided to use the Battery Energy Management (BEM) code on their cars. The BEM code is an identifying code for the battery that must be registered into the car’s BMS (Battery Management System) using the battery registration tool.

What is BMS (Battery Management System) Technology?
The term BMS refers to Battery Management Systems that are used to control and monitor the performance of rechargeable batteries, such as EFB and AGM-type batteries. Here’s an explanation of BMS technology-
Battery Protection
BMS technology protects batteries against various harmful circumstances, such as overcharging, over-discharging, short circuits, and high temperatures. BMS guarantees that the battery works within safe limits by monitoring and managing the charging and discharging processes.
Balancing
BMS technology can balance individual cells in multi-cell battery packs to guarantee they have the same charge level. Balancing improves the battery pack’s overall capacity and lifespan.
SOC & SOH Monitoring
BMS systems continually monitor the battery’s State of Charge (remaining capacity) and State of Health (overall condition).
Temperature Control
Some BMS systems contain temperature sensors to monitor and control the battery’s temperature. Temperature regulation is critical since overheating may be harmful and reduce battery life.
Applications of BMS Technology
HEV Cars –
A gasoline engine and an electric motor power Hybrid Electric Vehicles. All battery energy is obtained by regenerative braking.
PHEV Cars –
An engine and an electric motor power Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Like ordinary hybrids, they can recharge their batteries via regenerative braking. However, they are different from normal hybrids in that they have a much larger battery and can be recharged by plugging into the grid.
BEV Cars –
Battery Electric cars, commonly known as EVs, are entirely electric cars with rechargeable batteries and no gasoline engine. The battery pack, which is recharged from the grid, provides all of the car’s energy.